November 4 2019: A survey on the e-procurement space recently done by leading e-procurement company C1 India suggests that over the next 5 years, e-procurement will present numerous opportunities to businesses. Businesses that exploit such opportunities will add value to their models.
Technologies like robotics, AI, and blockchain will make procurement more intelligent, efficient and transform it from a tactical differentiator to a strategic one. Data will be continuously cleansed and improved using machine learning techniques. This will leverage process outcomes and automatically identify and cure data anomalies in systems. Manual processes for high-volume and regular procurement tasks will be eliminated. Procurement will become seamless end-to-end.
Procurement will happen over hyper-connected ecosystems which will become the standard. The process from sourcing to settlement will be unified and provide business agility and speed.
Last year organizations adopted cognitive procurement technologies like big data analytics, machine learning, natural language processing, artificial intelligence, and robotic process automation. In 2019 these technologies are being adopted more aggressively. Blockchain is being used to transform procurement by improving contract management, tracking, and payment processing.
Before e-procurement organizations communicated offline. Today e-procurement lets organizations work in a coordinated environment. Organizations today are likely to communicate in real-time using online platforms. Organizations use AI to source strategically by predicting demand and during advanced negotiation techniques to optimise their search for suppliers.
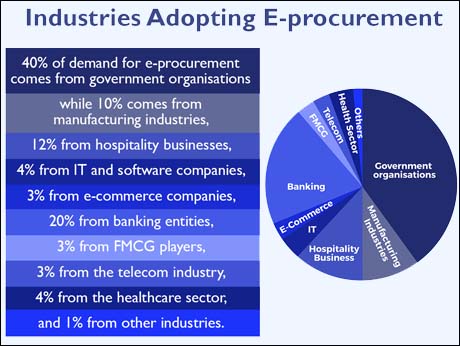
Industries Adopting E-procurement : 40% of demand for e-procurement comes from government organisations while 10% comes from manufacturing industries, 12% from hospitality businesses, 4% from IT and software companies, 3% from e-commerce companies, 20% from banking entities, 3% from FMCG players, 3% from the telecom industry, 4% from the healthcare sector, and 1% from other industries.