Prof K.R. Srivathsan, Pro Vice Chancellor of the Indira Gandhi National Open University – the world’s largest distance education initiative -- is a pioneer thinker in educational networking for India. In an earlier role, he inspired and steered the work on the KISSAN agricultural information network in Kerala state and today is helping to realise another bold vision: Vedyadhara, an open education framework. We are privileged to share with our readers, Prof Srivathsan’s suggestions for a nationwide knowledge network, leveraging on existing networks to build a truly inclusive knowledge society in India
We need a multi-pronged solution to manage the very large scale National Skills Development Mission that is intended to generate 500 million trained youths in India by 2022. Such a solution must leverage the state-of-the-art ICT, the large investments in connectivity, broadband, e-governance, mobile services etc. The system proposed here, promotes freedom for innovations with accountability and quality assurance. Though it is proposed for the National Skills Mission, it is equally applicable for higher education, continuing education, etc.
Three tiers of organization are proposed:
• Tier-1: National Centre for Technology Enhanced Education (NCTEE) to be established directly under the Advisor for the NSDM.
• Tier-2: Convergence Institute for Learning and Knowledge (CILK) – one (minimum) in each state.
• Tier-3: Leaf end organizations and Study/Training Centres who conduct the programmes. Each such organization may be domain specific or geography specific with one or more study centres, colleges or extension services units.
• Further, NCTEE will serve as the base for a National Consortium along the lines of NASSCOM in the skills, vocational education and Community Knowledge Enterprises (CKE) areas.
Under the NCTEE we establish the Vedyadhara Open Education Framework (VOEF) over cloud servers accessible to all 3-Tiers of organizations through the broadband, e-Governance and mobile network. VOEF will be used as the reference technology augmented education management framework for all programmes under the NSDM.
The CILK in each state will - Establish, supervise and manage the VOEF and offer IT enabled services for the multitude of skills, vocational, continuing and higher education programmes offered by different organizations, universities and government that will be conducted in the Tier-3 organizations. This will include local language facilitations and mass media support services.
- Promote massive capacity building in relevant ICT capabilities to support a large number of 'Community Knowledge Enterprises' (CKE) in the areas of Health, Education, Agriculture, Rural Development and Tourism and Culture (we call them together as the HEART areas).
- Assist incubating the CKEs in the districts to employ the persons who are trained under the vocational education.
- Be co-located with IGNOU Regional Centre in the concerned state. This will also help service the IT enabled services for IGNOU's programmes and those offered in the Community colleges.
OVERVIEW OF VEDYADHARA FRAMEWORK The Vedyadhara Open Education Framework has been piloted in IGNOU. It is an extension of the systems and concepts of Education Grid and KISSAN-Kerala developed earlier by the author at IIITM-Kerala, Trivandrum. The core of Vedyadhara is that each education programme offered by any organization (very large like 1000s of learners in a single course to small with 10s of students) is considered to be a CKE.
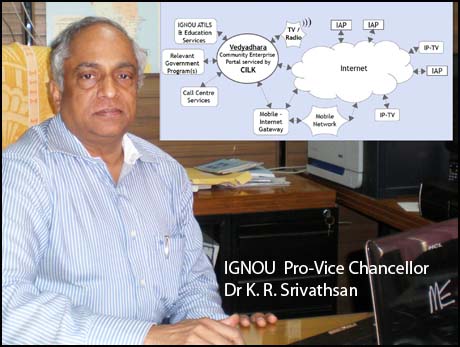
All systems and suites of VOEF are implemented using well known and robust cloud based Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) like the Wikis, Linux Virtualization, any common database, Blogs and Discussion Forums, etc. These are both Indian Languages unicode compliant as well as exploit the Web 2.0 for community services. Further VOEF anticipates seamless access and collaboration of communities reached through any mode of access – Internet, IP-TV, mobile, tablets, etc. as illustrated in the figure ( see inset in main photo with this article). VOEF leverages on convergence over broadband and mobile over Internet and mass media.
VOEF is an excellent and unified ICT enabled services delivery model for education management, CKEs and citizens centred e-governance. VOEF is an inclusive framework where the community of users (e.g. Teachers, resources, learners) on one side, the programme management and web resources on the other are seamlessly linked. Proprietary or programme specific software and applications may readily be included in the backend of VOEF.
Establishing VOEF in all education programmes calls for large national efforts in capacity building for both individuals and organizations. VOEF is an inclusive ICT framework for smart communities and knowledge enterprises. Each education programme is taken to be a knowledge enterprise.
CILK The proposed Convergence Institute for Learning and Knowledge (CILK) is a necessary constructive intervention to ensure and assure well coordinated education programmes management jointly by the organizations that offer the programmes, the government and the places where these programmes are offered. Further it will facilitate the localization and content and knowledge sharing within the language region and across languages.
CILK is a facilitation institute for all the education and training organizations in a state. It will also channel large national and industry offered programmes across the country. By itself CILK does not have degree or diploma granting authority. CILK will support both IT enabled educational and CKE services. CILK allows for disciplined use of ICT and educational/services processes using ICT in every programme. We propose to co-locate the same with IGNOU's Regional Centres as IGNOU itself will need CILK services for its programmes reach.
CILK will also be a powerful channel for corporates through their CSR route to offer capacity building and entrepreneurship development by establishing CKEs. Various Government programmes and training needs of working employees and officials will also benefit by using the CILK services. CILK may be used to establish 'knowledge corridors' as adjunct to industry corridors and PURA (Provision of Urban Amenities in Rural Areas) concepts.
While there will be many programmes offered by different organizations, there are a few areas that are of immense importance for education, employment and development, particularly in the rural and small town areas of the country. The areas are (i) Healthcare; (ii) Education; (iii) Agriculture;
(iv) Rural Development; and (v) Tourism and Culture. We call them as HEART areas.
There are a large number of plan and other programmes of the government in these areas. Examples are Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana; Janani Suraksha Yojana; MNREGA, NRHM, NACO, SSA and RMSA, etc. All these and many more will immensely benefit from the ICT facilitaition in both capacity building and rural entrepreneurship using the Vedyadhara Framework for both education and CKE in these areas.
We shall refer to the adapted VOEF for CKEs as Vedyadhara Community Enterprises Framework (VCEF). Although both VOEF and VCEF have much in common in terms of IT enabled systems and services, the two serve complementary needs. One is for education and the other for community enterprises. In the sense that education too should be viewed as CKE, the two may be considered isomorphic.
The Big Vision: Linking Education and Employment through CKEs
Here are sample CKEs that are readily be established through CILK using VOEF and VCEF.
Healthcare: Emergency Medical Care; Blood Bank Services, Mother and Child Care; Health Assurance and Evidence Based Medicine practice, etc. NRHM programmes to be integrated into this CKE framework in every Pnachayath.
Education: The management of ICT in schools, colleges, for learners support, etc. requires great deal technology support services. These may be managed through CKEs set up for the purpose.
Agriculture: Extension services of diverse Agricultural organizations, ICAR, the krishi bhavans, KVKs, commodity boards and exchanges, weather and other advisories, knowledge management in specific agricultural sectors localized for every panchayath are all candidates for CKEs. We may also have local Virtual Farm Cooperatives of groups of farmers in a region feeding into agri¬processing and marketing enterprises.
Rural Development: Drinking Water supply, MNREGA, Watershed Management, local development programmes of diverse kinds, disaster management, etc.
Tourism and Culture: Promotion of IT services for tourists visiting the panchayath with linked services; online multimedia publishing of local and traditional arts, crafts and culture, linking to realtime events, GIS based navigation aids for tourists, better coordination of local pilgims spots and events, etc.
We may focus on about 10 CKEs in each panchayat each employing about 20 well trained skills and vocational professionals. These make at least 200 persons employed in the IT enabled CKEs. With 100,000 panchayats, this translates into employing 20 million trained personnel across the country to drive the knowledge economy. The proposed network of 1 million CKEs will usher India into the most potent exemplar of a knowledge society.
Prof KR Srivathsan received Bachelor's degree from the Regional Engineering College (now NIT) Durgapur in West Bengal, MTech from IIT Kanpur and PhD from Queen’s University, Canada — all in electrical engineering. He was Professor and Head of the Electrical Engineering Department at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-Kanpur. He took over as first Director of the Indian Institute of Information Technology and Management, Kerala, in December 2000. Prof Srivathsan joined IGNOU as Pro-Vice Chancellor on November 1, 2008. He is Member, Board of Management, IGNOU and the Board of the Distance Education Council and is working to establish the Advanced Centre for Informatics and Innovative Learning (ACIIL) under IGNOU.
He is actively involved in launch of open courses jointly by the National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) and IGNOU, and building the National Education Grid that would modernise both open distance education and conventional education through technology-enhanced learning and teaching systems.
Prof Srivathsan has been associated with India's progress in Networking, Internet and IT since the mid-Eighties. He was a founding member and coordinator of ERNET in the eighties and early nineties. He was a core team member that established the first campus-wide LAN in the country in the eighties.
September 16 2011